本文介绍如何使用集成到斯坦福 CoreNLP(一个用于自然语言处理的开源库)中的情感工具在 Java 中实现此类任务。
斯坦福 CoreNLP 情感分类器
要执行情感分析,您需要一个情感分类器,这是一种可以根据从训练数据集中学习的预测来识别情感信息的工具。
在斯坦福 CoreNLP 中,情感分类器建立在递归神经网络 (RNN) 深度学习模型之上,该模型在斯坦福情感树库 (SST) 上进行训练。
SST 数据集是一个带有情感标签的语料库,从数千个使用的句子中推导出每个句法上可能的短语,从而允许捕获文本中情感的构成效果。简单来说,这允许模型根据单词如何构成短语的含义来识别情绪,而不仅仅是通过孤立地评估单词。
为了更好地了解 SST 数据集的结构,您可从斯坦福 CoreNLP 情感分析页面下载数据集文件。
在 Java 代码中,Stanford CoreNLP 情感分类器使用如下。
首先,您通过添加执行情感分析所需的注释器(例如标记化、拆分、解析和情感)来构建文本处理管道。 就斯坦福 CoreNLP 而言,注释器是一个对注释对象进行操作的接口,其中后者表示文档中的一段文本。 例如,需要使用 ssplit 注释器将标记序列拆分为句子。
斯坦福 CoreNLP 以每个句子为基础计算情绪。 因此,将文本分割成句子的过程始终遵循应用情感注释器。
一旦文本被分成句子,解析注释器就会执行句法依赖解析,为每个句子生成一个依赖表示。 然后,情感注释器处理这些依赖表示,将它们与底层模型进行比较,以构建带有每个句子的情感标签(注释)的二值化树。
简单来说,树的节点由输入句子的标记确定,并包含注释,指示从句子导出的所有短语的从非常消极到非常积极的五个情感类别中的预测类别。 基于这些预测,情感注释器计算整个句子的情感。
设置斯坦福 CoreNLP
在开始使用斯坦福 CoreNLP 之前,您需要进行以下设置:
要运行斯坦福 CoreNLP,您需要 Java 1.8 或更高版本。
下载 Stanford CoreNLP 包并将该包解压缩到您机器上的本地文件夹中。
下载地址:
https://nlp.stanford.edu/software/stanford-corenlp-latest.zip
本文以将上述代码解压到如下目录为例:
c:/softwareInstall/corenlp/stanford-corenlp-4.3.2
完成上述步骤后,您就可以创建运行斯坦福 CoreNLP 管道来处理文本的 Java 程序了。
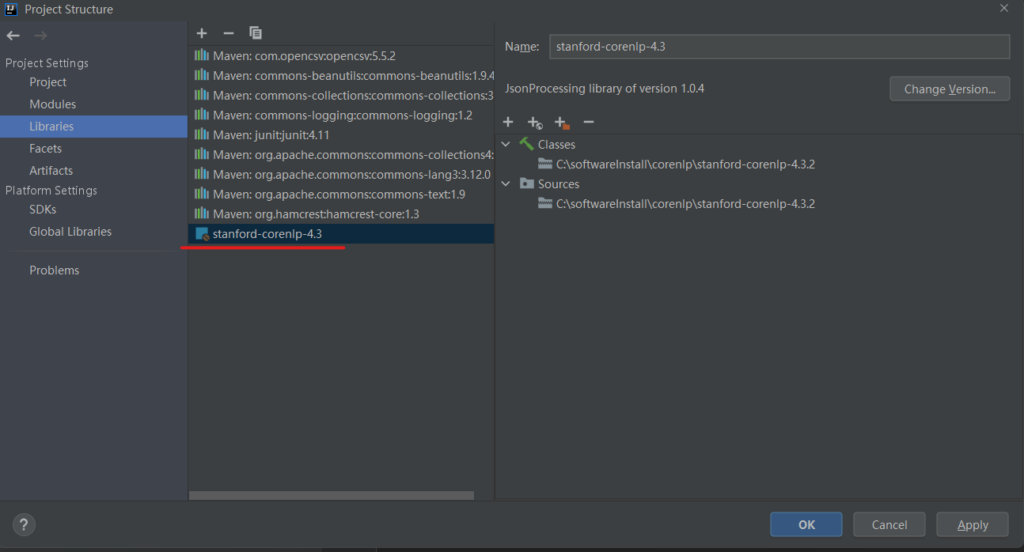
首先新建一个maven项目,并手动将stanford-corenlp-4.3.2添加到Libraries中:
在以下示例中,您将实现一个简单的 Java 程序,该程序运行斯坦福 CoreNLP 管道,以对包含多个句子的文本进行情感分析。
首先,实现一个NlpPipeline类,该类提供初始化管道的方法和使用此管道将提交的文本拆分为句子然后对每个句子的情感进行分类的方法。 下面是NlpPipeline类代码:
package com.zh.ch.corenlp;
import edu.stanford.nlp.ling.CoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.neural.rnn.RNNCoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.pipeline.Annotation;
import edu.stanford.nlp.pipeline.StanfordCoreNLP;
import edu.stanford.nlp.sentiment.SentimentCoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.trees.Tree;
import edu.stanford.nlp.util.CoreMap;
import java.util.Properties;
public class NlpPipeline {
StanfordCoreNLP pipeline = null;
public void init()
{
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("annotators", "tokenize, ssplit, parse, sentiment");
pipeline = new StanfordCoreNLP(props);
}
public void estimatingSentiment(String text)
{
int sentimentInt;
String sentimentName;
Annotation annotation = pipeline.process(text);
for(CoreMap sentence : annotation.get(CoreAnnotations.SentencesAnnotation.class))
{
Tree tree = sentence.get(SentimentCoreAnnotations.SentimentAnnotatedTree.class);
sentimentInt = RNNCoreAnnotations.getPredictedClass(tree);
sentimentName = sentence.get(SentimentCoreAnnotations.SentimentClass.class);
System.out.println(sentimentName + "\t" + sentimentInt + "\t" + sentence);
}
}
}init() 方法初始化StanfordCoreNLP 管道,它还初始化使用该情感工具所需的分词器、依赖解析器和句子拆分器。 要初始化管道,请将带有相应注释器列表的 Properties 对象传递给 StanfordCoreNLP() 构造函数。 这将创建一个定制的管道,准备好对文本执行情感分析。
在NlpPipeline类的estimatingSentiment()方法中,调用之前创建的管道对象的process()方法,传入文本进行处理。 process() 方法返回一个注释对象,该对象存储对提交的文本的分析。
接下来,迭代注释对象,在每次迭代中获得一个句子级 CoreMap 对象。对于这些对象中的每一个,获取一个包含用于确定底层句子情绪的情绪注释的 Tree 对象。
将 Tree 对象传递给 RNNCoreAnnotations 类的 getPredictedClass() 方法,以提取对应句子的预测情绪的编号代码。然后,获取预测情绪的名称并打印结果。
要测试上述功能,请使用调用 init() 方法的 main() 方法实现一个类,然后调用 nlpPipeline 类的 estimatingSentiment() 方法,将示例文本传递给后者。
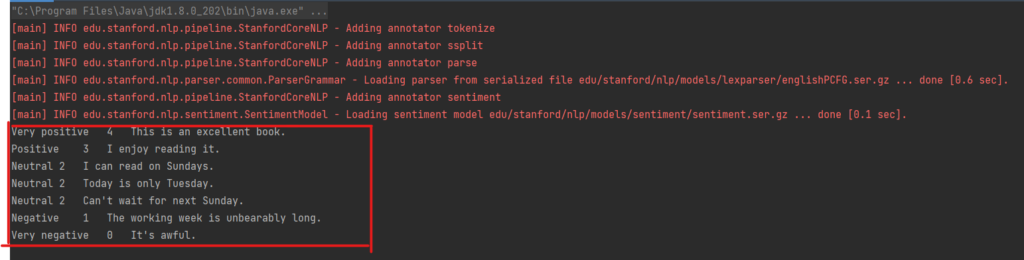
在以下实现中,为了简单起见,直接指定text文本。示例句子旨在涵盖斯坦福 CoreNLP 可用的整个情绪评分范围:非常积极、积极、中立、消极和非常消极。
package com.zh.ch.corenlp;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
static NlpPipeline nlpPipeline = null;
public static void processText(String text) {
nlpPipeline.estimatingSentiment(text);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String text = "This is an excellent book. I enjoy reading it. I can read on Sundays. Today is only Tuesday. Can't wait for next Sunday. The working week is unbearably long. It's awful.";
nlpPipeline = new NlpPipeline();
nlpPipeline.init();
processText(text);
}
}执行结果:
分析在线客户评论
正如您从前面的示例中了解到的,Stanford CoreNLP 可以返回句子的情绪。 然而,有许多用例需要分析多段文本的情绪,每段文本可能包含不止一个句子。 例如,您可能想要分析来自电子商务网站的推文或客户评论的情绪。
要使用斯坦福 CoreNLP 计算多句文本样本的情绪,您可能会使用几种不同的技术。
在处理推文时,您可能会分析推文中每个句子的情绪,如果有一些正面或负面的句子,您可以分别对整个推文进行排名,忽略带有中性情绪的句子。 如果推文中的所有(或几乎所有)句子都是中性的,则该推文可以被列为中性。
然而,有时您甚至不必分析每个句子来估计整个文本的情绪。 例如,在分析客户评论时,您可以依赖他们的标题,标题通常由一个句子组成。
要完成以下示例,您需要一组客户评论。 您可以使用本文随附的 NlpBookReviews.csv 文件中的评论。 该文件包含在 Amazon Review Export 的帮助下从 Amazon 网页下载的一组实际评论,这是一个 Google Chrome 浏览器扩展程序,允许您将产品评论及其标题和评级下载到逗号分隔值 (CSV) 文件中 . (您可以使用该工具探索一组不同的评论以进行分析。)
将下述代码添加到NlpPipeline中
public String findSentiment(String text) {
int sentimentInt = 2;
String sentimentName = "NULL";
if (text != null && text.length() > 0) {
Annotation annotation = pipeline.process(text);
CoreMap sentence = annotation
.get(CoreAnnotations.SentencesAnnotation.class).get(0);
Tree tree = sentence
.get(SentimentCoreAnnotations.SentimentAnnotatedTree.class);
sentimentInt = RNNCoreAnnotations.getPredictedClass(tree);
sentimentName = sentence.get(SentimentCoreAnnotations.SentimentClass.class);
}
return sentimentName;
}您可能会注意到,上面的代码类似于上一节中定义的 estimatingSentiment() 方法中的代码。 唯一的显着区别是这次您没有迭代输入文本中的句子。 相反,您只会得到第一句话,因为在大多数情况下,评论的标题由一个句子组成。
下述代码将从 CSV 文件中读取评论并将它们传递给新创建的 findSentiment() 进行处理,如下所示:
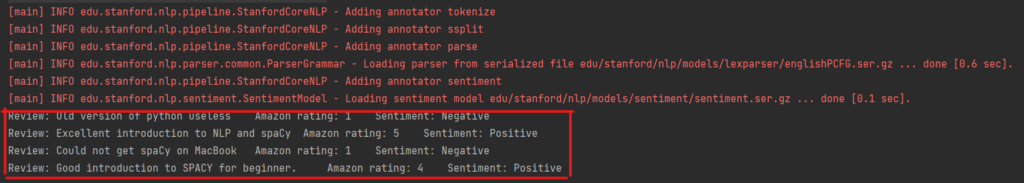
public static void processCsvComment(String csvCommentFilePath) {
try (CSVReader reader = new CSVReaderBuilder(new FileReader(csvCommentFilePath)).withSkipLines(1).build())
{
String[] row;
while ((row = reader.readNext()) != null) {
System.out.println("Review: " + row[1] + "\t" + " Amazon rating: " + row[4] + "\t" + " Sentiment: " + nlpPipeline.findSentiment(row[1]));
}
}
catch (IOException | CsvValidationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}执行结果:
完整代码:
NlpPipeline.java
package com.zh.ch.corenlp;
import edu.stanford.nlp.ling.CoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.neural.rnn.RNNCoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.pipeline.Annotation;
import edu.stanford.nlp.pipeline.StanfordCoreNLP;
import edu.stanford.nlp.sentiment.SentimentCoreAnnotations;
import edu.stanford.nlp.trees.Tree;
import edu.stanford.nlp.util.CoreMap;
import java.util.Properties;
public class NlpPipeline {
StanfordCoreNLP pipeline = null;
public void init() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("annotators", "tokenize, ssplit, parse, sentiment");
pipeline = new StanfordCoreNLP(props);
}
public void estimatingSentiment(String text) {
int sentimentInt;
String sentimentName;
Annotation annotation = pipeline.process(text);
for(CoreMap sentence : annotation.get(CoreAnnotations.SentencesAnnotation.class))
{
Tree tree = sentence.get(SentimentCoreAnnotations.SentimentAnnotatedTree.class);
sentimentInt = RNNCoreAnnotations.getPredictedClass(tree);
sentimentName = sentence.get(SentimentCoreAnnotations.SentimentClass.class);
System.out.println(sentimentName + "\t" + sentimentInt + "\t" + sentence);
}
}
public String findSentiment(String text) {
int sentimentInt = 2;
String sentimentName = "NULL";
if (text != null && text.length() > 0) {
Annotation annotation = pipeline.process(text);
CoreMap sentence = annotation
.get(CoreAnnotations.SentencesAnnotation.class).get(0);
Tree tree = sentence
.get(SentimentCoreAnnotations.SentimentAnnotatedTree.class);
sentimentInt = RNNCoreAnnotations.getPredictedClass(tree);
sentimentName = sentence.get(SentimentCoreAnnotations.SentimentClass.class);
}
return sentimentName;
}
}Main.java
package com.zh.ch.corenlp;
import com.opencsv.CSVReader;
import com.opencsv.CSVReaderBuilder;
import com.opencsv.exceptions.CsvValidationException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
static NlpPipeline nlpPipeline = null;
public static void processCsvComment(String csvCommentFilePath) {
try (CSVReader reader = new CSVReaderBuilder(new FileReader(csvCommentFilePath)).withSkipLines(1).build())
{
String[] row;
while ((row = reader.readNext()) != null) {
System.out.println("Review: " + row[1] + "\t" + " Amazon rating: " + row[4] + "\t" + " Sentiment: " + nlpPipeline.findSentiment(row[1]));
}
}
catch (IOException | CsvValidationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void processText(String text) {
nlpPipeline.estimatingSentiment(text);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String text = "This is an excellent book. I enjoy reading it. I can read on Sundays. Today is only Tuesday. Can't wait for next Sunday. The working week is unbearably long. It's awful.";
nlpPipeline = new NlpPipeline();
nlpPipeline.init();
// processText(text);
processCsvComment("src/main/resources/NlpBookReviews.csv");
}
}
相关推荐




0评论