本文主要介绍了MySQL数据库闭包Closure Table表实现示例,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧
1、 数据库闭包表简介
像MySQL这样的关系型数据库,比较适合存储一些类似表格的扁平化数据,但是遇到像树形结构这样有深度的数据,就很难驾驭了。
针对这种场景,闭包表(Closure Table )是最通用的设计,它要求一张额外的表来存储关系,使用空间换时间的方案减少操作过程中由冗余的计算所造成的消耗。
闭包表,它记录了树中所有节点的关系,不仅仅只是直接父子关系,它需要使用两张表,除了节点表本身之外,还需要使用一张关系表,用来存储祖先节点和后代节点之间的关系(同时增加一行节点指向自身),并且根据需要,可以增加一个字段,表示深度。
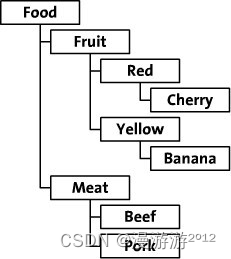
以下图数据举例说明:
2、创建节点表
drop table if exists node; CREATE TABLE `node` ( `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `pid` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `name` varchar(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '名称', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='节点表';
3、创建关系表
drop table if exists node_tree_paths; CREATE TABLE `node_tree_paths` ( `ancestor` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '祖先节点', `descendant` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '后代节点', `distance` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '祖先距离后代的距离', PRIMARY KEY (`ancestor`,`descendant`), KEY `descendant` (`descendant`), CONSTRAINT `ancestor` FOREIGN KEY (`ancestor`) REFERENCES `node` (`id`), CONSTRAINT `descendant` FOREIGN KEY (`descendant`) REFERENCES `node` (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='节点关系表';
4、创建存储过程添加数据
drop procedure if exists AddNode; CREATE PROCEDURE `AddNode`(_parent_name varchar(255), _node_name varchar(255)) BEGIN DECLARE _ancestor INT; DECLARE _descendant INT; DECLARE _parent INT; IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT id From node WHERE name = _node_name) THEN -- 入库 INSERT INTO node (name) VALUES(_node_name); -- 入库ID SET _descendant = (select @@IDENTITY); -- 自己到自己的链信息 INSERT INTO node_tree_paths (ancestor,descendant,distance) VALUES(_descendant, _descendant,0); -- 上级是否存在 IF EXISTS (SELECT id FROM node WHERE name = _parent_name) THEN SET _parent = (SELECT id FROM node WHERE name = _parent_name); INSERT INTO node_tree_paths (ancestor,descendant,distance) SELECT ancestor,_descendant,distance+1 from node_tree_paths where descendant = _parent; END IF; END IF; END
5、插入测试数据
call AddNode('', '中国');
call AddNode('中国', '华东');
call AddNode('中国', '华南');
call AddNode('中国', '华西');
call AddNode('中国', '华北');
call AddNode('华东', '江苏');
call AddNode('华东', '浙江');
call AddNode('华东', '山东');
call AddNode('华东', '安徽');
call AddNode('华东', '江西');
call AddNode('江苏', '南京');
call AddNode('南京', '六合区');6、查询 华东 下所有的子节点
SELECT n3.name FROM node n1 INNER JOIN node_tree_paths n2 ON n1.id = n2.ancestor INNER JOIN node n3 ON n2.descendant = n3.id WHERE n1.name = '华东' AND n2.distance != 0
7、查询 华东 下直属子节点
SELECT n3.name FROM node n1 INNER JOIN node_tree_paths n2 ON n1.id = n2.ancestor INNER JOIN node n3 ON n2.descendant = n3.id WHERE n1.name = '华东' AND n2.distance = 1
8、查询 六合区 所处的层级
SELECT n2.*, n3.name FROM node n1 INNER JOIN node_tree_paths n2 ON n1.id = n2.descendant INNER JOIN node n3 ON n2.ancestor = n3.id WHERE n1.name = '六合区' ORDER BY n2.distance DESC
9、闭包表的优缺点和适用场景
优点:在查询树形结构的任意关系时都很方便。
缺点:需要存储的数据量比较多,索引表需要的空间比较大,增加和删除节点相对麻烦。
适用场合:纵向结构不是很深,增删操作不频繁的场景比较适用。
发表评论 取消回复